FileSystemObject also called FSO, provides an easy object-based model to access a computer’s file system. You simply have to create an instance of FileSystemObject in VBA and then you can generate files, read files, delete files, iterate through folders, and do many other operations on your computer’s file system.
The FileSystemObject is present inside the Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library i.e. Scrrun.dll. This DLL supports the creation and manipulation of files using TextStream object and this is the reason why FSO doesn’t support operation on binary files.
Uses of File System Object
FileSystemObject can be used for multiple tasks such as:
- Creating, opening, reading, writing, and deleting text files.
- Creating, altering, and deleting folders.
- Iterating files and folders.
- Copying and moving files or folders.
- Checking if a location (file path) exists or not.
Accessing FileSystemObject
The FileSystemObject comprises several object collections and each of these object collections contains information about a specific aspect of the file system. These collections are:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Drive | This object allows you to get information about a drive attached to your system. For instance, it can tell you the space available in a drive, its logical name, etc. Note that the drive object that we are referring to here doesn’t necessarily mean the hard disk, it can be a CD-ROM, Flash drive, RAM, or even a logically connected drive via LAN. |
| Folder | This object allows you to create, delete, move, or query a folder hierarchy. |
| File | This object allows you to create, delete, move, or query a File. |
| TextStream | TextStream object allows you to read or write text files. |
So, diagrammatically a FileSystemObject can be shown as:
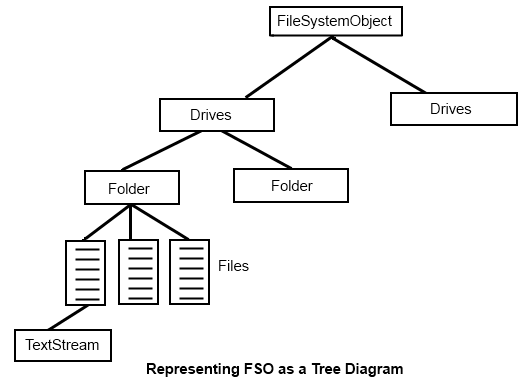
Please note that FSO communicates with most of the above objects indirectly. It just directly contains the object collection for “Drives”. Each “Drive” object in the “Drives” collection contains a chain of “Folder” objects. And each “Folder” object contains a “File” collection.
To make it more meaningful, let’s say it this way: A FileSystemObject contains three main methods to fetch (read) specific information about Drives, Folders, or Files, these methods are GetDrive, GetFolder and GetFile respectively. Now let’s say you need to find the file size of a particular file, so you will create an instance of the GetFile method and then fetch its size property.
Note: GetDrive, GetFolder and GetFile are not the only methods inside FSO, I have just used them to explain things. In the below section we will see all the methods contained inside FileSystemObject.
FSO Methods
The below table gives details about various FileObjectSystem methods and the tasks they perform:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| GetDrive, GetFolder, and GetFile | These methods are used for fetching information about Drive, Folders, and Files respectively. |
| CreateFolder and CreateTextFile | Helps in creating new folders or files. |
| DeleteFile and DeleteFolder | Helps in deleting existing files or folders. |
| CopyFile and CopyFolder | These methods help in copying files or folders from one location to another. |
| MoveFile and MoveFolder | These methods help in moving files or folders from one location to another. |
Creating a FileSystemObject in VBA: In this section, we will deal with two things:
- Creating a reference of Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library i.e. Scrrun.dll
- Creating an FSO Object.
Creating a reference of Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library
To create a reference of Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library follow the below steps:
- First of all, open the VBA editor by pressing “Alt + F11”.
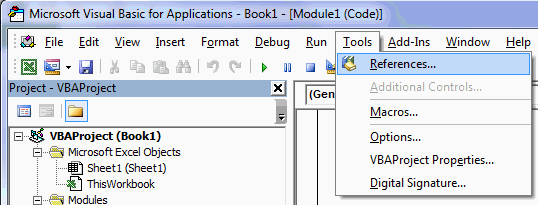
- Next, navigate to “Tools” > “Reference” as shown above.
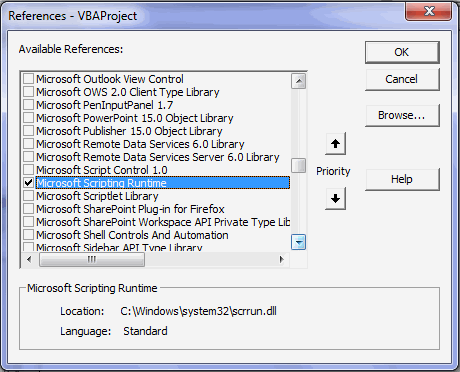
- This will open a reference window. Here select and check the entry “Microsoft Scripting Runtime” and click “OK”.
- Now the reference to Microsoft Scripting Runtime Library has been added.
Creating an FSO Object
Creating an FSO object is simple, follow the below steps to do this:
- In the VBA editor navigate to “Insert” > “Module”.
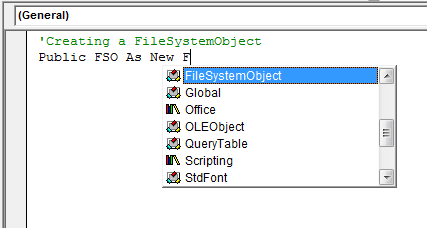
- Now in the module window type “
Public FSO As New FileSystemObject”. - This will create an object of FileSystemObject with the name FSO.
After this, you can simply access the FileSystemObject’s methods using the FSO object.
6 Practical Examples of accessing FileSystemObject
Now let’s move to some practical examples of FSO:
Example 1: Use FSO to find the total free space of a drive.
Below is the code to do this:
'Creating a FileSystemObject
Public FSO As New FileSystemObject
Sub DiskSpace()
Dim drv As Drive
Dim Space As Double
Set drv = FSO.GetDrive("C:") 'Creating the the Drive
object Space = drv.FreeSpace
Space = Space / 1073741824 'converting bytes to GB
Space = WorksheetFunction.Round(Space, 2) 'Rounding
MsgBox "C: has free space = " & Space & " GB"
End Sub
Explanation: In this code first we have created a Drive object using ‘GetDrive’ Method and then we have used its ‘FreeSpace’ property to fetch the free space.
Finally, we have displayed the free space using a message box.
Note that there are two properties to fetch the free space of a drive i.e. drv.FreeSpace and drv.AvailableSpace.
Example 2: Check if a folder exists or not. If the folder doesn’t exists then create that folder.
Below is the code:
'Creating a FileSystemObject
Public FSO As New FileSystemObject
Sub ChkFolder()
Dim Fldr_name As String
Fldr_name = InputBox("Enter the path of the folder to check :")
If Len(Fldr_name) > 0
Then If FSO.FolderExists(Fldr_name) = True Then
MsgBox "Folder Exists!"
Else FSO.CreateFolder (Fldr_name)
MsgBox ("Folder Created!")
End If Else MsgBox "Wrong Input"
End If
End Sub
Explanation: In the code, we have used an InputBox function to get the path of the folder from the user. After this using the If statement along with FolderExists the method, we have checked whether that folder is present or not. If the folder is not present then we create that folder using the CreateFolder method.
Note: CreateFoldermethod will only create a single folder at a time. So, if you supply an argument “C:\Folder1\Folder2\Folder3” to it then it will only create the Folder3 inside Folder2. But if Folder2 doesn’t exist then it will throw a path not found an error.
Example 3: Write a code using FSO to copy a folder from one location to another.
Below is the code to accomplish this:
'Creating a FileSystemObject Public FSO As New FileSystemObject Sub CopyFolder() FSO.CopyFolder "C:\Source-Folder\", "D:\Destination-Folder\", True MsgBox "Copying Done!" End Sub
Explanation: In the code, we have used the CopyFolder method of FSO, this method accepts three arguments:
- Source Path
- Destination path
- A Boolean argument to specify Overwrite Existing.
Example 4: Using FileSystemObject fetch the Temp directory, System folder, and Windows folder.
To do this we can use the below code:
'Creating a FileSystemObject
Public FSO As New FileSystemObject
Sub GetFolderpath()
Dim Windows_Fldr As String
Dim System_Fldr As String
Dim Temp_Fldr As String
Windows_Fldr = FSO.GetSpecialFolder(0)
System_Fldr = FSO.GetSpecialFolder(1)
Temp_Fldr = FSO.GetSpecialFolder(2)
MsgBox ("Windows folder path = " & Windows_Fldr & vbNewLine & _ "System folder path = " & System_Fldr & vbNewLine & _ "Temp folder path = " & Temp_Fldr)
End Sub
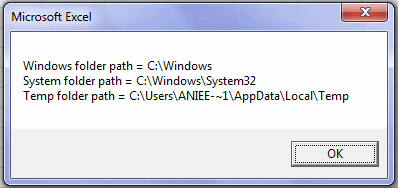
GetSpecialFolder method of FSO, this method accepts a single numerical argument i.e. 0-2.
FSO.GetSpecialFolder(0)– Fetches the path of Windows Folder.FSO.GetSpecialFolder(1)– Fetches the path of System Folder.FSO.GetSpecialFolder(2)– Fetches the path of the Local Temporary folder.
Example 5: Create a text file, write some content to it, then read the file, and finally delete the file.
Below is the code to accomplish this:
'Creating a FileSystemObject Public
FSO As New FileSystemObject
Sub CreateFile()
Dim txtstr As TextStream
Dim FileName As String
Dim FileContent As String
Dim File As File
FileName = "C:\TestDirectory\File.txt" 'File to be created
'Creating a file and writing content to it
FileContent = InputBox("Enter the File Content")
If Len(FileContent) > 0 Then
Set txtstr = FSO.CreateTextFile(FileName, True, True)
txtstr.Write FileContent
txtstr.Close
End If
' Reading from the file that we have just created
If FSO.FileExists(FileName) Then
Set File = FSO.GetFile(FileName)
Set txtstr = File.OpenAsTextStream(ForReading, TristateUseDefault)
MsgBox txtstr.ReadAll txtstr.Close
' Finally Deleting the File
File.Delete (True)
End If
End Sub
Explanation: This code first creates a text file, adds content to it, then reads it, displays it using a message box, and finally deletes that file.
Example 6: Write a VBA Code that can iterate all the files present inside a folder and also fetches their size and modified date.
The following code can accomplish this task:
'Creating a FileSystemObject
Public FSO As New FileSystemObject
Sub ListFiles()
'Declaring variables
Dim objFolder As Folder
Dim objFile As File
Dim strPath As String
Dim NextRow As Long
'Specify the path of the folder
strPath = "C:\Users\Aniee\Desktop\ExcelTrick\ "
'Create the object of this folder
Set objFolder = FSO.GetFolder(strPath)
'Check if the folder is empty or not
If objFolder.Files.Count = 0 Then
MsgBox "No files were found...", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
'Adding Column names for A, B, and C
Cells(1, "A").Value = "File Name"
Cells(1, "B").Value = "Size"
Cells(1, "C").Value = "Modified Date/Time"
'Find the next available row
NextRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row + 1
'Loop through each file in the folder
For Each objFile In objFolder.Files
'List the name, size, and date/time of the current file
Cells(NextRow, 1).Value = objFile.Name
Cells(NextRow, 2).Value = objFile.Size
Cells(NextRow, 3).Value = objFile.DateLastModified
'Find the next row NextRow = NextRow + 1
Next objFile
End Sub
Explanation: In this code, we have created a Folder object and then we are iterating all its files using For Each loop. From the file object, we are fetching the Name, Size and DateLastModified properties and finally we are writing them to the active worksheet. So, this was all about FileSystemObject and how to use it in VBA. Do share your comments related to the topic.





